KCET 2020 Physics Paper with Solutions
The Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) is an annual state-level examination conducted for admission into various undergraduate programs in colleges across Karnataka. Physics is one of the core subjects in the KCET exam, carrying significant weightage. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of the KCET 2020 Physics paper, providing insights, solutions, and tips to help aspirants ace this section of the exam.
Importance of Physics in KCET exam
Physics plays a crucial role in the KCET exam as it assesses candidates’ understanding of fundamental concepts in the subject. Proficiency in Physics is essential for engineering and other science-related fields, making it imperative for aspirants to perform well in this section to secure admission into their desired courses.
Overview of the Physics paper structure
Physics paper 2024 Solved
- a. Domains are all perfectly aligned.
- b. Magnetic moment of each molecule is zero.
- c. The individual molecules have non-zero magnetic moment which are all perfectly aligned.
- d. Domains are partially aligned.
Solution:
Answer: a
Due to thermal agitation, with increase in temperature randomness of the molecules increases and magnetic field moments get partially aligned. Hence the domains are partially aligned.
2. A rod of length 2 m slides with a speed of 5 ms-1 on a rectangular conducting frame as shown in figure. There exists a uniform magnetic field of 0.04 T perpendiculars to the plane of the figure. If the resistance of the rod is 3Ω then the current through the rod is
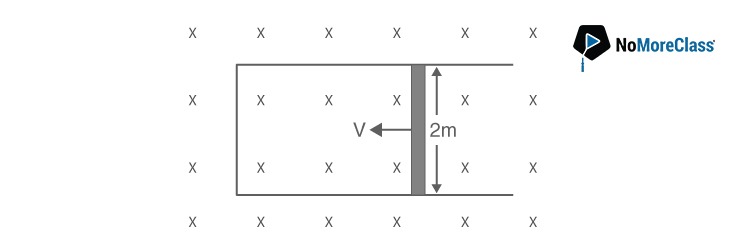
- a. 1.33 A
- b. 75mA
- c. 133 mA
- d. 0.75 A
Solution:
Answer: c
We know that the current, i = Blv/R= (0.04×2×5)/3 = 133 mA
3. The ratio of magnetic field at the centre of a current carrying circular coil to its magnetic moment is ‘x’. If the current and the radius both are doubled then the new ratio will become
- a. x/8
- b. 2x
- c. 4x
- d. x/4
Solution:
Answer: a
Magnetic field at the center of the current carrying loop is given by B=(μ0/4π)×(2πi/a)=(μ0 i)/2a.
Magnetic moment at the center of the current carrying loop is given by M=iπa2
thus B/M=μ0/(2πa3 )=x (given) when both current and radius are doubled ratio become x/8 times.
4. In the given circuit the peak voltages across C, L and R are 30 V, 110 V and 60 V respectively. The rms value of the applied voltage is
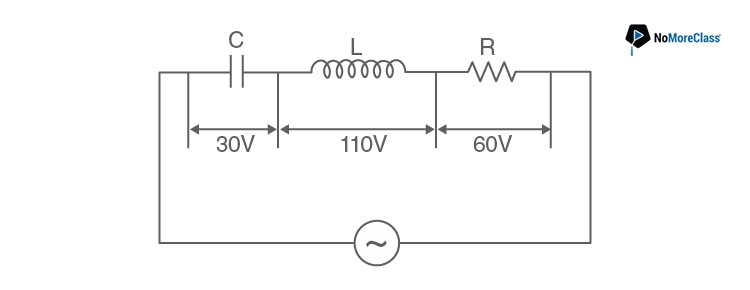
- a. 141 V
- b. 100 V
- c. 200 V
- d. 70.7 V
Solution:
Answer: d
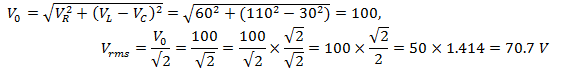
5. The power factor of R-L circuit is
- a.
- b.
- c.
- d.
Solution:
Answer: c
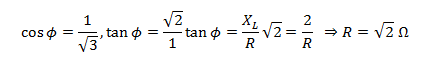
6. In the given circuit, the resonant frequency is
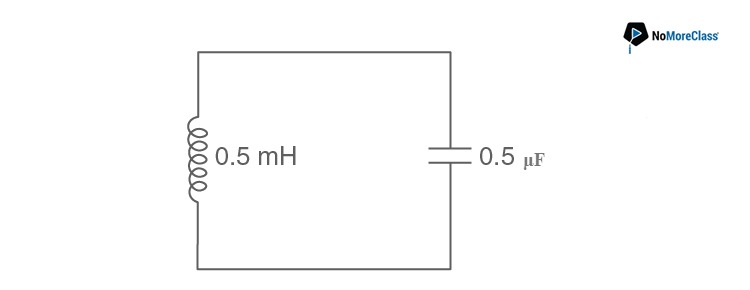
- a. 15910 Hz
- b. 15.92 Hz
- c. 159.2 Hz
- d. 1592 Hz
Solution:
Answer: d
Resonant frequency of an circuit is given by
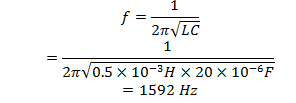
7. The current in a coil of inductance 0.2 H changes from 5 A to 2 A in 0.5 sec. The magnitude of the average induced emf in the coil is
- a. 0.3 V
- b. 0.6 V
- c. 1.2 V
- d. 30 V
Solution:
Answer: c
Average induced emf, ϵ=L dI/dt
=0.2 ((5-2)/0.5)=(2/5) × 3=1.2 V
8. An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed
- a. Moves towards the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
- b. Moves away from the lens with uniform speed.
- c. Moves away from the lens with uniform acceleration.
- d. Moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
Solution:
Answer: d
Velocity of image in convex lens Vi=(f/(f+u))2 Vo and image will move from focus to infinity (i.e. away from the lens).
From the formula, velocity of image
(dVi)/dt=(dVi/du)×(du/dt)=2(f/f+u)f ln (f+u)× 5 (because du/dt=5 m/s)
⇒(dVi)/dt=10f2 ln(f+u)/(f+u)
We can see that acceleration of image ∝ln(f+u), i.e varies with distance of object
So the image moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration
9. The refracting angle of a prism is A and refractive index of material of prism is cot
- a. 1800 – 2A
- b. 1800 – 3A
- c. 1800 + 2A
- d. 900– A
Solution:
Answer: a
10. A light beam of intensity
- a. 1.2 X 10-5 kg ms-1
- b. 2 X 10-5 kg ms-1
- c. 1 X 10-5 kg ms-1
- d. 5 X 10-5 kg ms-1
Solution:
Answer: d
11. Three polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are kept parallel to each other such that the angle between pass axes of P1and P2 is 450 and that between P2 and P3 is 450. If unpolarised beam of light of intensity 128 Wm-2 is incident on P1. What is the intensity of light coming out of P3?
- a. 64Wm-2
- b. 128 Wm-2
- c. 0
- d. 16 Wm-2
Solution:
Answer: d
We have unpolarised beam’s intensity I0=128w/m2
Using Malu’s law we have I=I0 cos2 θ
When beam passed from the first polaroid, I=I0/2
Again, as the angle between p1 and p2 is 450, beam intensity when it will pass p2 would be I1=I0/2 cos2450=I0/4
And, also the angle between p2 and p3 is 450, beam intensity when it will come out of p3 will be I2=I0/4 cos2 450=I0/8=128/8=16w/m2
12. Two poles are by a distance of 3.14 m. The resolving power of human eye is minute of an arc. The maximum distance from which he can identify the two poles distinctly is
- a. 376 m
- b. 10.8 km
- c. 5.4 km
- d. 188 m
Solution:
Answer: b
Given the lateral separation of the poles d=3.14 m
The resolving power of the eye is θ=1min=π/(60×180) rad
The maximum distance from which poles are distinctly visible is D=d/θ
⇒D=(3.14×60×180)/π=10800m=10.8 km
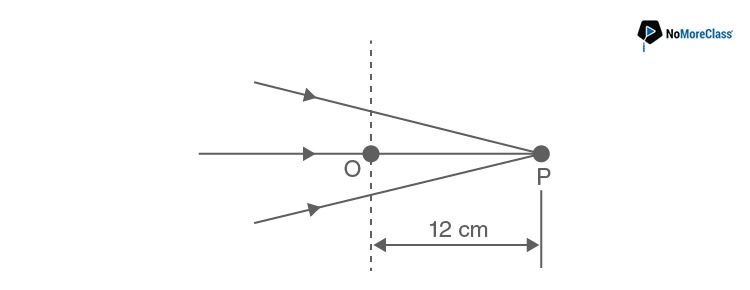
- a. 48 cm
- b. 12 cm
- c. 24 cm
- d. 36 cm
Answer: a
So, here when we put the concave lens, let the beam will converge at a distance x=v
Using lens formulae, we have, 1/f=1/v-1/u
Where u=12 cm and f=-16 cm is given
∴1/v=(1/f)+(1/u)=(-1/16)+(1/12)=1/48 cm⇒ v=48 cm
Hence, x=48 cm
14. The de-Broglie wavelength associated with electron of hydrogen atom in this ground state is
- a. 10A0
- b.0.3Ao
- c. 3.3Ao
- d.6.26Ao
Solution:
Answer. c
De-Broglie wavelength is given by λ=12.27/√E0, where E0 is the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom whose value is 13.6 V
∴λ=12.27/(√1 3.6)=3.33 Ǻ
15. The following graph represents the variation of photo current with anode potential for a metal surface. Here I1, I2 and I3 represents intensities and Y1, Y2 and Y3 represent frequency for curves 1, 2 and 3 respectively, then
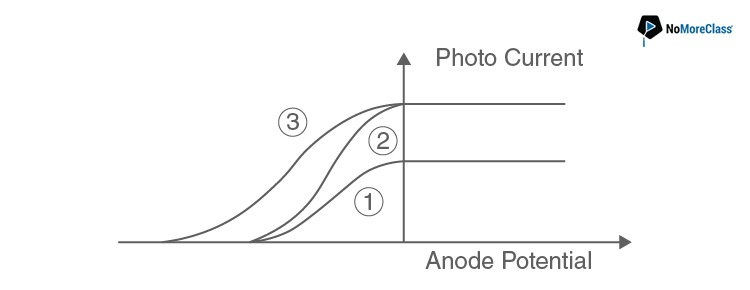
- a. Y2= Y3 and I1=I3
- b. Y1 = Y2 and I1≠ I2
- c. Y1 = Y3 and I1 = I3
- d. Y1 = Y2 and I1 = I2
Solution:
Answer: b
Here in the graph we can see that, the Stopping potential is same for 1 and 2. So, frequencies will be same i.e. γ1=γ2 and, currents are different. So, intensity are different i.e. I1≠I2.
16. In Young’s Double Slit Experiment, the distance between the slits and the screen is 1.2 m and the distance between the two slits is 2.4 mm. If a thin transparent mica sheet of thickness 1μm and R.I of 1.5 is introduced between one of the interfering beams, the shift in the position of central bright fringe is
- a. 0.25 mm
- b. 2 mm
- c. 0.5 mm
- d. 0.125 mm
Solution:
Answer: a
Path difference due to insertion of mica sheet Δx=(μ-1)t
Let the shift in the fringe pattern be ‘y’
Also, path difference Δx=y×d/D, so comparing both (μ-1)t=y×(d/D)
y=(μ-1)t×(D/d) , where μ=1.5,D=2.4 and d=1.2 putting the values, we get
y= 0.25 mm.
17. Angular momentum of an electron in hydrogen atom is
- a. 6.8 eV
- b. 4.35 eV
- c. 1.51 eV
- d. 3.4 eV
Solution:
Answer: c
Angular momentum,
L= nh/2π=3h/2π ,
which is given in the problem, also n=3
∴E=13.6/n2 eV
⇒ E=13.6/32 =1.51 eV.
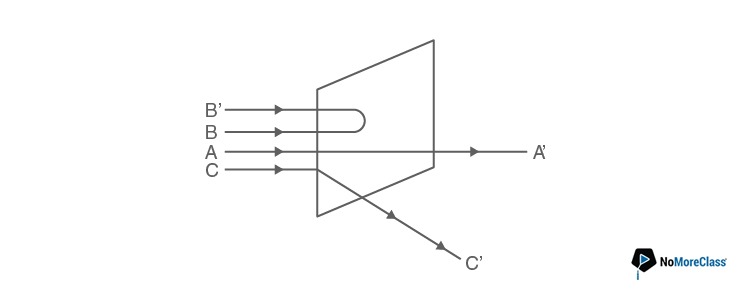
- a. C’ will be minimum and in B’ maximum
- b. B’ will be minimum and in C’ maximum
- c. A’ will be maximum and in B’ minimum
- d. A’ will be minimum and in B’ maximum
Solution:
Answer: c
A’ will be maximum and B’ will be minimum, because atom is hollow and whole mass of the atom is concentrated in a small centre called nucleus.
19. The period of revolution of an electron revolving in nth orbit of H-atom is proportional to
- a. Independent of n
- b. n2
- c.
- d. n3
Solution:
Answer: d
As we know that time period of revolution of an electron is T=2πr/v,
And r∝n2/Z2 and v ∝Z/n
∴T∝n3/Z2 and for H-atom Z=1, T∝n3
- a. A proton in the nucleus decays emitting an electron
- b. An atomic electron is electron is ejected
- c. An electron which is already present within the nucleus is ejected
- d. A neutron in the nucleus decays emitting an electron
Solution:
Answer: d
During β– decay, a neutron in the nucleus decays emitting an electron.
21. A radio-active element has half-life of 15 years. What is the fraction that will decay in 30 years?
- a. 0.85
- b. 0.25
- c. 0.5
- d. 0.75
Solution:
Answer: d
Fraction undecayed is given as,
N/N0 =(1/2) (t/T)
Here, t=30 years and T=15 years
So,
N/N0 =(1/2)((30 years)/(15 years))
or, N/N0 =(1/2)2
or, N/N0 =1/4
Therefore,
Fraction undecayed =1-N/N0
or, Fraction undecayed =1- (1/4)
or, Fraction undecayed =3/4=0.75
22. Two protons are kept at a separation of 10 nm. Let Fn and Fe be the nuclear force and the electromagnetic force between them
- a. Fe and Fn differ only slightly
- b. Fe=Fn
- c. Fe>>Fn
- d. Fe<<Fn
Solution:
Answer: c
Nuclear forces are short range force existing in the range of a 10-15 m. If the separation between the particles is greater than 10 -15 m, nuclear force is negligible.
Therefore, at a separation of 10 nm, the electromagnetic force is greater than the nuclear force.
Hence, Fe≫Fn
23. In the following circuit what are P and Q:
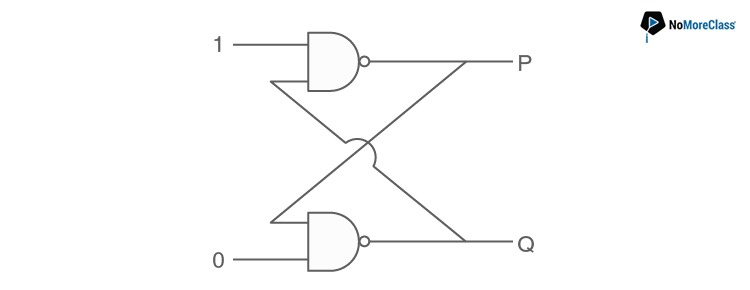
- a. P = 1, Q = 1
- b. P = 1, Q = 0
- c. P = 0, Q = 1
- d. P = 0, Q = 0
Solution:
Answer: c
A NAND gate gives an output 1 if at least one of the inputs is zero.
Hence Q is 1.
Therefore, the inputs for the upper NAND gate are 1, 1.
Hence P=0.
24. A positive hole in a semiconductor is
- a. an artificially created particle
- b. an anti-particle of electron
- c. a vacancy created when an electron leaves a covalent bond
- d. absence of free electrons
Solution:
Answer: c
A positive hole in a semiconductor is a vacancy which is created at the site of a covalent bond when an electron leaves a covalent bond.
25. A 220 V A.C. supply is connected between points A and B as shown in figure what will be the potential difference V across the capacitor?
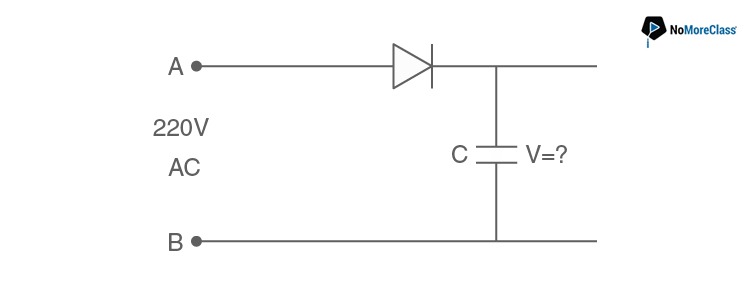
- a.
- b. 220 V
- c. 110 V
- d. 0
Solution:
Answer: a
During the positive half cycles of input ac, a p-n junction diode is forward biased and hence it conducts.
While during the negative half cycles, the diode will be reverse biased and hence does not conduct.
The capacitor is charged to maximum potential difference.
Therefore, the potential difference across capacitor C is equal to the peak value of the applied ac voltage, i.e.,
V=Vmax
or, V=√2 Vrms
or, V=√2×220 V=200 √2 V
26. Two long straight parallel wires are a distance 2d apart. They carry steady equal currents flowing out of the plane of the paper. The variation of magnetic field B along the line xx’ is given by
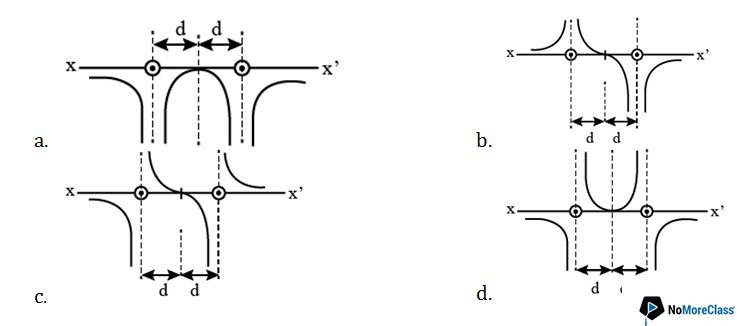
Solution:
Answer: c
The magnetic field due to a long straight current carrying wire is given by,
B=(μ0 I)/2πr
or, B ∝1/r
At the point exactly mid-way between the conductors, the net magnetic field is zero. Using right hand thumb rule, we find that the magnetic field due to left wire will be in j ̂direction while due to the right wire is in (-j ̂ ) direction.
Magnetic field at a distance x from the left wire, lying between the wires.
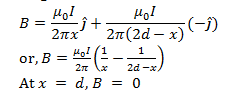
For x<d, B is along j ̂
For x>d, B is along (-j ̂)
On the left side of the left conductor, magnetic fields due to the currents will add up and the net magnetic field will be along (-j ̂) direction.
To the right side of second conductor, the total magnetic field will be along j ̂ direction.
27. At a metro station, a girl walks up a stationary escalator in 20 sec. If she remains stationary on the escalator, then the escalator takes her up in 30 sec. The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be
- a. 10 sec
- b. 25 sec
- c. 60 sec
- d. 12 sec
Solution:
Answer: d
Let, the length of the escalator be L.
Velocity of the girl, vg=L/t1 =L/20
Velocity of the escalator, ve = L/t2 = L/30
On moving escalator,
vnet = vg + ve
or, vnet = (L/20)+(L/30)
or, vnet = L/12
Since, vnet = L/t
Therefore,
L/t = L/12
t = 12 s
28. Rain is falling vertically with a speed of 12 ms-1. A woman rides a bicycle with a speed of 12 ms-1 in east to west direction. What is the direction in which she should hold her umbrella?
- a. 45o towards West
- b. 30o towards East
- c. 45o towards East
- d. 30o towards West
Solution:
Answer: a
To protect herself from the rain, the woman must hold her umbrella in the direction of the relative velocity of the rain with respect to the woman.
tanθ = vw/vf = 12 m/s
or, tan θ = 1
or, θ = 450
Therefore, the direction in which she should hold her umbrella is 450 toward west.
29. A cylindrical wire has a mass (0.3 ± 0.003) g, radius (0.5± 0.005)mm and length (6± 0.06)cm. The maximum percentage error in the measurement of its density is
- a. 4
- b. 1
- c. 2
- d. 3
Solution:
Answer: a
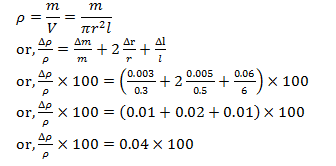
(Δρ/ρ) ×100=4%
Therefore, the percentage error in the measurement of density is 4.
30. A body is initially at rest. It undergoes one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration. The power delivered to it at time ‘t’ is proportional to
- a. t2
- b.
- c. t
- d.
Solution:
Answer: c
As we know,
P=Fv
where, P is the power, F is the force and v is the velocity.
or, P=mav
or, P=ma2 t
or, P∝t
31. A thin uniform rectangular plate of mass 2 kg is placed in x-y plane as shown in figure. The moment of inertia about x-axis is Ix = 0.2 kgm2 and the moment of inertia about y-axis is Iy= 0.3 kgm2. The radius of gyration of the plate about the axis passing through O and perpendicular to the plane of the plate is
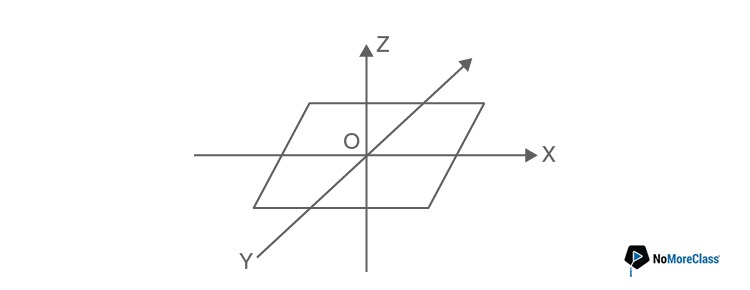
- a. 31.6 cm
- b. 50 cm
- c. 5 cm
- d. 38.7 cm
Solution:
Answer: b
By perpendicular axis theorem we know that,
Iz=Ix+Iy=0.3+0.2=0.5 kgm2
as we know that MOI
I=mK2⇒0.5=2×K2
K=1/2=0.5 m=50 cm.
32. One end of a string of length I is connected to a particle of mass ‘m’ and the other to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in a circle with speed ‘v’, the net force on the particle (directed towards the centre) is: (T is the tension in the string)
- a. 0
- b. T
- c.
- d.
Solution:
Answer: b
When a particle connected to a string revolves in a circular path around a centre, the centripetal force is provided by the tension produced in the string. Hence, in the given case, the net force on the particle is the tension T. (T=(mv2)/l)
33. Young’s modulus of a perfect rigid body is
- a. Between zero and unity
- b. Zero
- c. Unity
- d. Infinity
Solution:
Answer: b
Young’s modulus = stress/strain, and for a perfect rigid body we know that strain is equal to 0 and hence Young’s modulus of a perfect rigid body becomes Infinity.
34. A wheel starting from rest gains an angular velocity of 10 rad/s after uniformly accelerated for 5 sec. The total angle through which it has turned is
- a. 50 π rad about a vertical axis
- b. 25 rad
- c. 100 rad
- d. 25 π rad
Solution:
Answer: b
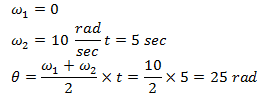
35. Iceberg floats in water with part of it submerged. What is the fraction of the volume of iceberg submerged if the density of ice is ρi = 0.917 g cm-3?
- a. 0
- b. 0.917
- c. 1
- d. 0.458
Solution:
Answer: b
Let V be the total volume of the iceberg and V’ of its volume be submerged into water
Floatation condition weight of iceberg = Weight of water displaced by submerged part by ice
Vρi g=V’ ρw g ⇒ V’/V =ρi/ρw =0.917/1=0.917
36. The value of acceleration due to gravity at a height of 10 km from the surface of earth is x. At what depth inside the earth is the value of the acceleration due to gravity has the same value x?
- a. 15 km
- b. 5 km
- c. 20 km
- d. 10 km
Solution:
Answer: c
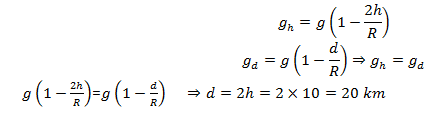
37. In an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas the product of pressure and volume.
- a. At first increases and then decreases
- b. Decreases
- c. Increases
- d. Remains constant
Solution:
Answer: b
In an adiabatic expansion as temperature decreases from an ideal gas equation PV=nRT.
Product of pressure and volume also decreases.
38. A certain amount of heat energy is supplied to a monoatomic ideal gas which expands at constant pressure. What fraction of the heat energy is converted into work?
- a.
- b. 1
- c.
- d.
Solution:
Answer: d
The heat Q is converted into the internal energy and work. According to the first law of thermodynamics, Q=U+W ⇒nCp Δt=nCv Δt+W
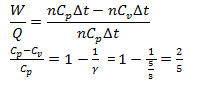
39. A sphere, a cube and a thin circular plate all of same material and same mass initially heated to same high temperature are allowed to cool down under similar conditions. Then the
- a. Cube will cool the fastest and plate the slowest.
- b. Plate will cool the fastest and cube the slowest.
- c. Sphere will cool the fastest and cube the slowest.
- d. Plate will cool the fastest and sphere the slowest.
Solution:
Answer: d
Surface area is more for plate and less for sphere. Hence plate will cool the fastest and sphere the slowest.
40. A train whistling at constant frequency ‘n’ is moving towards a station at a constant speed V. The train goes past a stationary observer on the station. The frequency ‘n’ of the sound as heard by the observer is plotted as a function of time ‘t’. Identify the correct curve
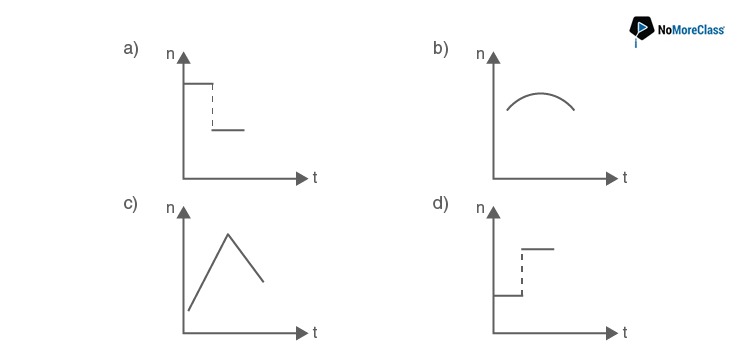
Solution:
Answer: a
As the train approaches the observer the apparent frequency is higher than the actual frequency. As the train moves away from the observer, the apparent frequency is lower than the actual frequency. Hence the correct option is (a).
41. A tray of mass 12 kg is supported by two identical springs as shown in figure. When the tray is pressed down slightly and then released, it executes SHM with a time period of 1.5 s. The spring constant of each spring is
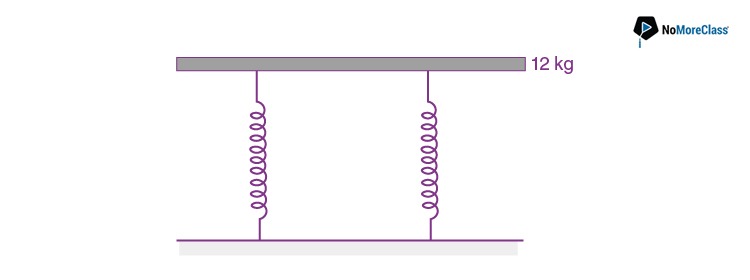
- a. ∞
- b. 50 Nm-1
- c. 0
- d. 105 Nm-1
Solution:
Answer: d
We know that
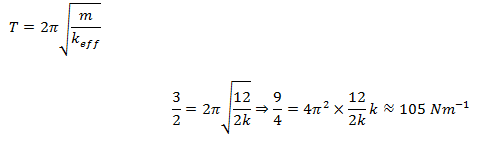
42. The electric field lines on the left have twice the separation on those on the right as shown in figure. If the magnitude of the field at A is 40 Vm-1, what is the force on 20 μC charge kept at B?
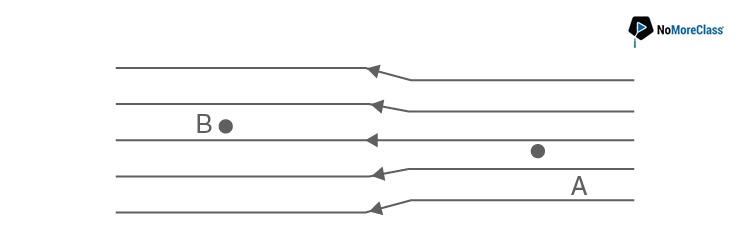
- a. 1 X 10-4V m-1
- b. 4 X 10-4 V m-1
- c. 8 X 10-4 V m-1
- d. 16 X 10-4 V m-1
Solution:
Answer: b
We know that F=qE =20×20 x 10-6 =4×10 -4 V/m.
43. An infinitely long thin straight wire has uniform charge density of
- a. 9 X 108NC-1
- b. 1.12 X 108 NC-1
- c. 4.5 X 108 NC-1
- d. 2.25 X 108 NC-1
Solution:
Answer: d
We know that
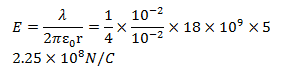
44. A point charge ‘q’ is placed at the corner of a cube side ‘a’ as shown in the figure. What is the electric flux through the face ABCD?
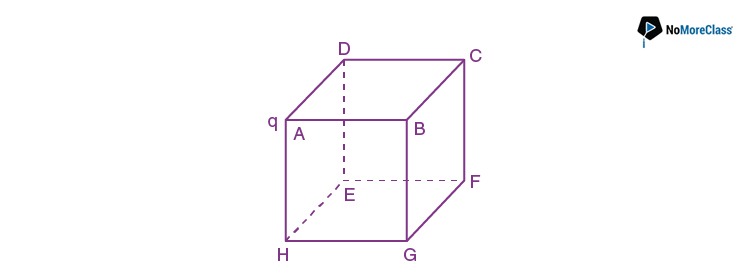
- a.
- b. 0
- c.
- d.
Solution:
Answer: b
Since the flux passing through face ABCD is parallel to that surface and area vector is perpendicular. Hence flux passing through ABCD is zero.
- a. 6 μF
- b. 2μF
- c. 3μF
- d. 4μF
Solution:
Answer: d
CP-CS=6 μF
2C-(C/2)=6
C=4 μF
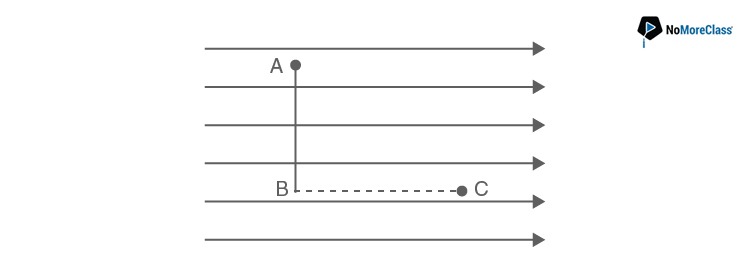
- a. VA>VB= VC
- b. VA=VB = VC
- c. VA=VB> VC
- d. VA =VB<VC
Solution:
Answer: c
Electric lines of force in an electric field always flow from a higher potential to a lower potential. Hence, VA=VB>VC
47. A dipole of dipole moment ‘p’ and moment of inertia I is placed in a uniform electric field
- a.
- b.
- c.
- d.
- Answer: c
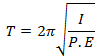
48. A hot filament liberates an electron with zero initial velocity. The anode potential is 1200 V. The speed of the electron when it strikes the anode is
- a. 2.5 X 108 ms-1
- b. 1.5 X 105 ms-1
- c. 2.5 X 106 ms-1
- d. 2.1 X 107 ms-1
Solution:
Answer: d
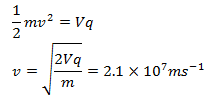
49. A metal rod of length 10 cm and a rectangular cross – section of
- a. Same irrespective of the three faces.
- b. Maximum when the battery is connected acrosscm faces.
- c. Maximum when the battery is connected acrosscm faces.
- d. Maximum when the battery is connected across 10 cm × 1 cm faces.
Solution:
Answer: b
Resistance is inversely proportional to area.
Hence resistance will be maximum when the battery is connected across 1 cm × (1/2) cm faces.
50. A car has a fresh storage battery of e.m.f. 12 V and internal resistance 2 X 10-2Ω. If the starter motor draws a current of 80 A. Then the terminal voltage when the starter is on is
- a. 9.3 V
- b. 12 V
- c. 8.4 V
- d. 10.4 V
Solution:
Answer: d
Hint: V=E-ir=10.4 V
51. When a soap bubble is charged,
- a. Its radius may increase or decrease.
- b. Its radius increases.
- c. Its radius decreases.
- d. The radius remains the same.
Solution:
Answer: b
When the radius of a soap bubble increases, the soap bubble gets charged.
52. The colour code for a carbon resistor of resistance 0.25k Ω± 10% is
- a. Red, Green, Silver
- b. Red, Grey, Brown, Silver
- c. Red, Green, Brown, Silver
- d. Red, Grey, Silver, Silver
Solution:
Answer: b
Red, Grey, Brown, Silver
- a.125Ω
- b.56Ω
- c.65Ω
- d.512Ω
Solution:
Answer: b
5/6 Ω
54. A potentiometer has a uniform wire of length 5 m. A battery of emf 10 V and negligible internal resistance is connected between its ends. A secondary cell connected to the circuit gives balancing length at 200 cm. The emf of the secondary cell is
- a. 8 V
- b. 4 V
- c. 6 V
- d. 2 V
Solution:
Answer: b
Emf of cell in the secondary circuit =potential gradient x balancing length
⇒(10/5) x 2 = 4V
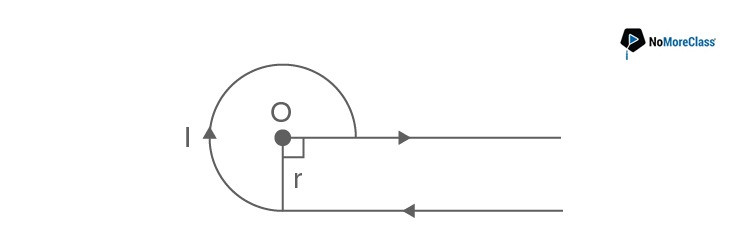
- a.38μoIr−μoI4πr
- b.34μoIr+μoI4πr
- c.310μoIr−μoI4πr
- d.38μoIr+μoI4πr
- Answer: d
56. The magnetic field at the origin due to a currentelement
- a.
- b.
- c.
- d.
Solution:
Answer: b
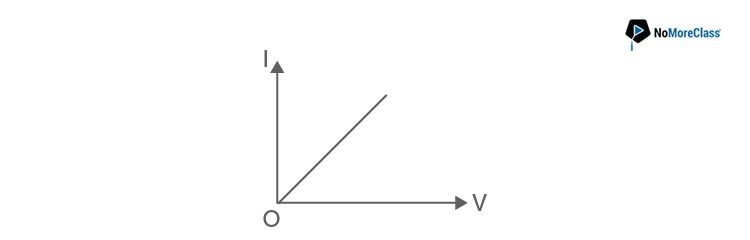
- a. Less if the length of the wire is increased.
- b. More if experiment is performed at higher temperature.
- c. More if a wire of steel of same dimension is used.
- d. Less if the area of the wire is increased.
Solution:
Answer: a
Slope = 1/R=A/ρl
Hence the slope becomes less if the length of the wire is increased.
58. A cyclotron is used to accelerate protons
- a. Same for all
- b. α – particle
- c. Proton
- d. Deuteron
Solution:
Answer: d
K.E. = q2/m
Hence, a deuteron gains the least kinetic energy.
59. A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetization of 8 Am-1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K. The magnetization will be
- a. 2.4 Am-1
- b.
- c.
- d. 6 Am-1
- Answer: c
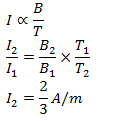
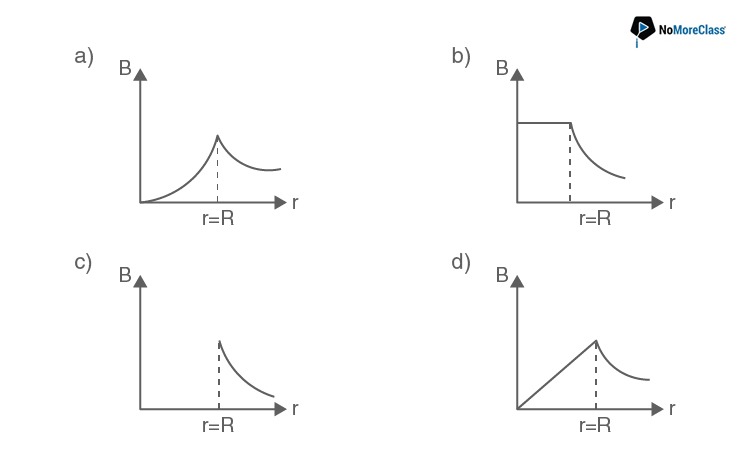
Solution:
Answer: a
The magnetic field increases as the point moves closer to the boundary of the wire and decreases as it moves away from the boundary of the wire.
Hence the correct option is (a).
- KCET 2019 Physics Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Maths Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Physics Paper
- KCET 2020 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Mathematics Questions Paper
- KCET Biology Examination 2021 Paper
- KCET – 2021 TEST PAPER
- IISER MOCK TEST – 4
- IISER MOCK TEST – 3
- IISER MOCK TEST – 2
- IISER MOCK TEST – 1
- KCET Mathematics- 2021 Test Paper
- KCET Chemistry – 2021 TEST PAPER
- KCET Physical – 2021 TEST PAPER
- KCET Biology Examination 2021 Paper
- KCET 2020 Mathematics Questions Paper
- KCET 2020 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Physics Paper
- KCET 2020 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Maths Paper with Solutions
