KCET 2019 Biology Paper with Solutions
Questions and answers of Biology paper
Question 1: What is the function of protein GLUT-4?
- a. Acts as an enzyme
- b. Enables glucose transport into cells
- c. Fight infectious agents
- d. Functions as intercellular ground substance
Solution:
Answer: (b)
GLUT4 is an insulin-responsive glucose transporter that is found in the adipose tissue, and brain. It is present in the cytoplasm of cells in vesicles from which it is translocated to the plasma membrane under the influence of insulin.
Question 2: Cell in the quiescent stage (G0)
- a. Always become cancerous
- b. Show indefinite proliferation
- c. Remain metabolically inactive
- d. Remain metabolically active
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In G0, some cells in the adult animals do not appear to exhibit division (e.g., heart cells) and many other cells divide only occasionally. These cells that do not divide further exist G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism.
Question 3: Consider the following statements i, ii, and iii regarding criteria for the essentiality of the nutrients in plants:
i. The presence of elements is must for plants to complete their life cycle.
ii. The role of the element can be replaced by another in their life cycle.
iii. The elements must be directly involved in the metabolism of the plant.
Choose the correct statement/s:
- a. i and iii
- b. i and ii
- c. iii only
- d. ii and iii
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The criteria for the essentiality of an element are given below:
(a) The element must be absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of the element, the plants do not complete their life cycle or set the seeds.
(b) The requirement of the element must be specific and not replaceable by another element. In other words, deficiency of any one element cannot be met by supplying some other element.
(c) The element must be directly involved in the metabolism of the plant.
Question 4: During the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP in photosynthesis:
- a. The protons accumulate in the intermembrane space of chloroplast
- b. The proton gradient is not required
- c. The protons accumulate in the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion
- d. The protons accumulate within the lumen of the thylakoids
Solution:
Answer: (c)
During chemiosmotic synthesis, ATP synthesis is linked to the development of a proton gradient across a membrane. This time these are membranes of the thylakoid. There is one difference though, here the proton accumulation is towards the inside of the membrane, i.e., in the lumen. In respiration, protons accumulate in the intermembrane space of the mitochondria when electrons move through the ETS.
Question 5: When tripalmitin is used as a respiratory substrate. The process consumes 145 molecules of oxygen and releases 102 molecules of CO2, then RQ would be
- a. 0.5
- b. 0.7
- c. 1.4
- d. 1.0
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio can be defined as the ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed during respiration. The value of respiratory quotient depends on the type of respiratory substrate. Its value is one for carbohydrates. However, it is always less than one for fats as fats consume more oxygen for respiration than carbohydrates. It can be illustrated through the example of tripalmitin fatty acid, which consumes 145 molecules of O2 for respiration while 102 molecules of CO2 are evolved. The RQ value for tripalmitin is 0.7.
- a. They do not show any negative impact on crop plants
- b. They help to increase the use of synthetic pesticides
- c. They are significant in treating the ecologically sensitive area
- d. They do not affect non –target pests
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Biocontrol refers to the use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests. In modern society, these problems have been tackled increasingly by the use of chemicals – by use of insecticides and pesticides. These chemicals are toxic and extremely harmful, to human beings and animals alike, and have been polluting our environment (soil, groundwater), fruits, vegetables and crop plants.
Question 7: A farmer has applied chemical fertilisers in the crop field for many successive seasons, the crop growth was poor as soil lost its fertility. Suggest the suitable microorganism that replenishes the fertility of the soil in this field.
- a. Spirulina
- b. Nostoc
- c. Chlorella
- d. Spirogyra
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Blue-green algae such as nostoc are very good at fixing nitrogen in the soil. They grow in symbiotic association with the roots of the plant forming a legume where nitrogen fixation for the plant takes place. It provides the plant and the soil with nitrogen. It is an effective way of increasing the production of the plant along with soil fertility.
- a. Transfer of foreign gene to the host
- b. Selection of recombinants
- c. Making the host cells competent
- d. Cleaving the vector by REN
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Antibiotic resistance gene present in the vector is mainly used for the selection of transformed bacterial cell. This transformed bacterial cell contains a recombinant vector with an antibiotic resistance gene so that it can resist from the antibiotic (tetracycline) containing media. The non- transformed cell failed to survive in the antibiotic-containing media during the selection process.
- a. Cellulase
- b. Lysozyme
- c. Pectinase
- d. Chitinase
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In order to use the DNA for genetic engineering processes, it must be in pure form, free from other macromolecules. This is termed DNA isolation and is the pioneering step. Since the DNA is enclosed within the membranes, it is required to break open the cell to release DNA along with other macromolecules such as RNA, proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. and from this mixture, DNA is purified. A release of DNA from a cell is achieved by treating the cells or tissues with enzymes such as chitinase (fungus), etc. These enzymes degrade cell wall; plasma membrane degrading enzymes like lipase, etc., are also needed. Since, yeast is a fungus and fungal cell wall is made of chitin (fungal cellulose), isolation of DNA necessarily requires the use of enzyme chitinase.
Question 10: Identify the DNA sequence which can be cut using EcoRI.
- a. 5’TGCTTAGGTA3′
- b. 5’ACGAATTCAT3′
- c. 5’TGCTTAGGTA3′
- d. 3’ACGAATTCAT5′
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In the laboratory, restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA into smaller fragments. The cuts are always made at specific nucleotide sequences. Different restriction enzymes recognize and cut different DNA sequences. EcoRI is a restriction enzyme that cleaves DNA double helices into fragments at specific sites. It is also a part of the restriction-modification system. The DNA sequence can be cut using EcoRI is 3‘ACGAATTCAT5’, 5‘TGCTTAAGTA3’.
- a. Valine
- b. Phenylalanine
- c. Tyrosine
- d. Tryptophan
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Valine is code for GTC, GTA and GTG.
The codons UUU and UUC codes for phenylalanine only. This feature of the genetic code is called degenerate
Tyrosine is code for ATA, ATG
Tryptophan, encoded by a single codon UGG
- a. Rho factor
- b. Elongation factor
- c. Sigma factor
- d. Termination factor
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Sigma factor proteins promote binding of RNA polymerase to promoter sites within DNA sequences to allow for initiation of transcription. Sigma factors are specific for the gene and are affected by the cellular environment. Sigma factors can regulate at both the transcriptional and the translational level.
- a. 2968 genes
- b. 242 genes
- c. 231 genes
- d. 2898 genes
Solution:
Answer: (c)
According to salient features of the human genome project, the total number of genes in the human genome is estimated at 30,000, Chromosome 1 has most genes (2968), and the Y has the fewest (231).
- a. Skin shreds
- b. Erythrocytes
- c. Semen samples
- d. Hair Follicle
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Erythrocytes contain the pigment haemoglobin, which imparts the red colour to blood and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissues. In a crime investigation, the investigating officer collects different biological samples from the crime spot for DNA fingerprinting analysis. Skin shreds, semen sample and hair follicle are helpful in the DNA fingerprinting.
Question 15: A mature mRNA consists of bases without any stop codon in between. Calculate the number of amino acids coded by the mRNA during translation.
- a. 9000
- b. 299
- c. 300
- d. 450
Solution:
Answer: (c)
3 bases contain 1 codon
900 bases contain 300 codons
The number of amino acids coded by this mRNA during translation of 300 codes is 300.
Question 16: Which one of the following ecosystems has the highest annual net primary productivity?
- a. Desert
- b. Tropical deciduous forest
- c. Tropical rain forest
- d. Temperature evergreen forest
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The tropical rainforest is a hot, moist biome found near Earth’s equator. Tropical rainforests receive from 60 to 160 inches of precipitation that is fairly evenly distributed throughout the year. The tropical rainforest has the highest annual net primary productivity (9000 Kcal / m2 / yr). Net primary productivity is the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy.
Question 17: Of the total incident solar radiation of percentage photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) captured by the plants
- a. 10-20% of PAR only
- b. 2-10% of PAR only
- c. 0-10% of PAR only
- d. 30-40% of PAR only
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Source of energy in an ecosystem is solar energy. 50 per cent of the solar energy incident over Earth is present in PAR (photosynthetically active radiation). Almost 1 to 5 per cent of incident solar energy or 2 to 10 per cent of PAR is captured by photosynthetic organisms in the synthesis of organic matter.
- a. Earth Summit
- b. Kyoto protocol
- c. World Summit
- d. Montreal protocol
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, the Rio Summit, the Rio Conference, and the Earth Summit was a major United Nations conference held in Rio de Janeiro from 3 to 14 June 1992. More than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil. Earth Summit was created as a response for the Member States to cooperate together internationally on development issues after the Cold War.
- a. Urbanisation
- b. Industrialisation
- c. Mono cropping
- d. Jhum cultivation
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Slash and burn agriculture, commonly called as Jhum cultivation in the north-eastern states of India, has also contributed to deforestation. In slash and burn agriculture, the farmers cut down the trees of the forest and burn the plant remains. The ash is used as a fertilizer and the land is then used for farming or cattle grazing. After cultivation, the area is left for several years so as to allow its recovery. The farmers then move on to other areas and repeat this process.
Question 20: In an area where DDT has been used extensively, the population of birds declined significantly because –
- a. Birds became vulnerable to predators
- b. Birds stopped laying eggs
- c. Many of the eggs laid by birds showed pre-matured breaking
- d. Earthworms in the area got eradicated
Solution:
Answer: (c)
DDT was commonly used as a pesticide. On the prolonged use of the pesticide, there were many side effects observed. The plants were accumulated with these chemicals and the pesticide entered the food chain. The birds were affected due to the presence of the pesticide. The birds lay the eggs but due to the effect of this chemical, the eggshells were very thin. The shell break and the embryos did not develop. So, there was a failure in the hatching of the birds from the eggs.
Question 21: The brain capacity of Homo habilis
- a. 1800 cc
- b. Between 650 cc – 800 cc
- c. 900 cc
- d. 1400 cc
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Homo-habilis were first human-like being with 650-800cc cranial capacity.
- a. Co-evolution
- b. Divergent Evolution
- c. Micro Evolution
- d. Convergent Evolution
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Divergent evolution is the process whereby groups from the same common ancestor evolve and accumulate differences, resulting in the formation of new species. Divergent evolution creates homologous organs. Homologous organs are the organs which have a similar structure but different function. They also have the same developmental origin. For example, the thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of Cucurbita. Thorns and tendrils both are axillary in position and are the modifications of axillary buds. But they both perform different functions as thorns are for protection and tendrils are for support.
Question 23: Identify the incorrect statements.
- a. HIV is transmitted by mosquito bite
- b. Pneumonia is a bacterial disease
- c. Cancer is a non-infectious disease
- d. Ringworm is a fungal disease
Solution:
Answer: (a)
HIV can’t be transmitted through saliva, so it can’t be transmitted through a mosquito’s bite.
Bacterial pneumonia is an infection of your lungs caused by certain bacteria. The most common one is Streptococcus (pneumococcus).
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. It is a major cause of death in developed countries. Most cancers are non-infectious diseases caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Ringworm is a common infection of the skin and nails that is caused by fungus.
- a. IgG
- b. IgE
- c. IgM
- d. IgA
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is antibodies produced by the immune system. If you have an allergy, your immune system overreacts to an allergen by producing antibodies called Immunoglobulin E (IgE). These antibodies travel to cells that release chemicals, causing an allergic reaction. This can cause wheezing, itching, running nose, watery or itchy eyes, and other symptoms.
Question 25: A man was suffering from mental illness like depression and insomnia. Identify the drug which is normally used as medicine in such cases
- a. Morphine
- b. Lysergic Acid Diethylamides (LSD)
- c. Nicotine
- d. Heroine
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Drugs like barbiturates, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, lysergic acid diethyl amides (LSD), and other similar drugs, that are normally used as medicines to help patients cope with mental illnesses like depression and insomnia, are often used.
Question 26: Plants like Marchantia and Funaria produce gametes by mitosis, because
- a. They are gametophytes
- b. Plant body is haploid
- c. They are dioecious
- d. Gametophyte is diploid
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Liverworts usually grow in moist and shady habitats. The plant body is haploid. Thallus is dorsiventral and closely appressed to the substrate. Some members have tiny leaf-like appendages in two rows on the stem-like structures. For example Marchantia.
Gametophyte is the predominant stage of the life cycle of moss. The leafy stage develops from the protonema as a lateral bud. The leafy stage consists of upright, slender axes bearing spirally arranged leaves. It is attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids. The leafy stage bears sex organs. Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation and budding in the secondary protonema.
Question 27: Identify the asexual reproductive structure ‘M’ in the following diagram:
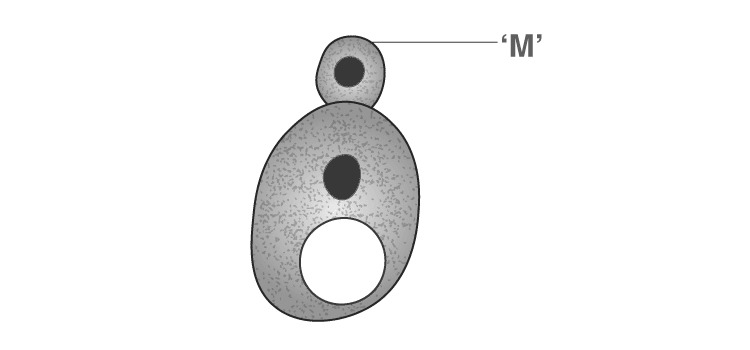
- a. Zoospore
- b. Bud
- c. Gemmule
- d. Conidium
Solution:
Answer: (b)
A single individual (parent) is capable of producing offspring. As a result, the offspring that are produced are not only identical to one another but are also exact copies of their parent is known as asexual reproduction.
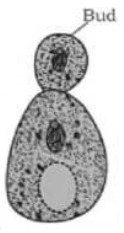
The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud.
- a. It attracts pollinators
- b. It facilitates self-pollination
- c. It prevents cross-pollination
- d. It facilitates cross-pollination
Solution:
Answer: (b)
In dichogamy, the anther and stigma mature at different times. Either anthers dehisce before the stigma becomes receptive (called protandry) or stigma becomes receptive before anthers dehisce (called protogyny). During this time, if pollen grains of another plant of the same species fall on the stigma of the dichogamy flower then, the type of pollination that will occur is cross-pollination.
- a. Synthetic seeds
- b. Production of Apomictic seeds
- c. Conventional plant breeding
- d. Parthenocarpy
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Conventional plant breeding is the development or improvement of cultivars using conservative tools for manipulating plant genome within the natural genetic boundaries of the species. The general strategy is to breed a cultivar whose genetic purity and productivity can be sustained by its natural mating system. Conventional plant breeding is used to overcome the problem of purchasing hybrid seeds.
- a. Artificial Pollination → Emasculation → Rebagging → Bagging
- b. Rebagging → Artificial Pollination → Bagging → Emasculation
- c. Emasculation → Bagging → Artificial Pollination → Rebagging
- d. Bagging → Artificial pollination → Rebagging → Emasculation
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Artificial hybridization is one of the major approaches to crop improvement programme. In such crossing experiments it is important to make sure that only the desired pollen grains are used for pollination and the stigma is protected from contamination (from unwanted pollen). This is achieved by emasculation and bagging techniques
The process of hybridization involves the following steps;
Emasculation
Baggin
Artificial Pollination
Rebagging
Question 31: Which of the following protozoan parasites causes sleeping sickness?
- a. Plasmodium
- b. Entamoeba
- c. Leishmania
- d. Trypanosoma
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In flagellated protozoans, the members of this group are either free-living or parasitic. They have flagella. The parasitic forms cause diseases such as sleeping sickness. Example: Trypanosoma.
Question 32: Which of the following phyla possess body cavity as shown in the diagram below?
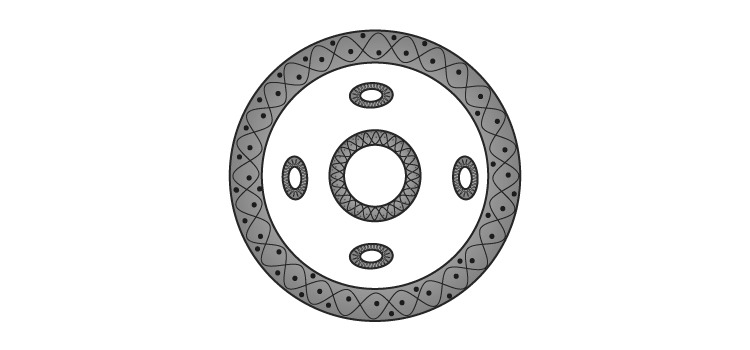
- a. Annelida
- b. Porifera
- c. Aschelminthes
- d. Coelenterata
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm; instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing them are called pseudocoelomates, e.g., aschelminthes
Question 33: Testa and Tegmen of the seed coat represent
- a. Dried integuments
- b. Dried Sepals
- c. Dried Tepals
- d. Dried petals
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The ovule maturation leads to the developmental changes in integuments in form of reduction and disorganization of the thickening. The ovules are covered with two layers of integuments. The outer integument is called as testa while inner integument is called as tegmen. The seeds are developmentally matured ovules containing two integument layers. The seed coat is developed from integuments which protect the embryo from mechanical injuries and desiccation. Testa and tegmen of the seeds coat represent two layers of dried integuments.
- a. The climatic conditions are uniform throughout the year
- b. The water stress is more
- c. The temperature is high
- d. The climatic conditions are not uniform throughout the year
Solution:
Answer: (a)
In plants of temperate regions, cambium is more active in spring and less active in autumn seasons. In temperate regions, climatic conditions are not uniform throughout the year. However, in tropics, climatic conditions are uniform throughout the year.
Question 35: Identify the part labelled as ‘M’ in the diagram given below:
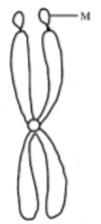
- a. Chromatid
- b. Kinetochore
- c. Centromere
- d. Satellite
Solution:
Answer: (d)
A few chromosomes have non-staining secondary constrictions at a constant location. This gives the appearance of a small fragment called the satellite i.e. M is represented as a satellite.
- a. Increases efficiency of mineral usage in plants
- b. Reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides
- c. Enhances the nutritional value of food
- d. Increases the post-harvest losses
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Genetically Modified or GM Crops are that type of plants whose DNA has been modified through genetic engineering for embedding a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. GM plants have been useful in many ways. Genetic modification has;
Made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, salt, heat).
Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops).
Helped to reduce post-harvest losses.
Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil).
Enhanced nutritional value of food, e.g., Vitamin ‘A’ enriched rice.
Question 37: Some multinational companies have exploited the traditional knowledge of the indigenous people to produce commercially important bioproducts, without their consent. This is an example of;
- a. Biopatent
- b. Bioprospecting
- c. Biopiracy
- d. Bioremediation
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Biopiracy is the term used to refer to the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organizations without proper authorization from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
Question 38: In Amphibian and reptiles, the body temperature changes corresponding to external temperature. The organisms which show this kind of response is termed as –
- a. Partial Regulators
- b. Regulators
- c. Thermophiles
- d. Conformers
Solution:
Answer: (b)
In regulator, organisms are able to maintain homeostasis by physiological (sometimes behavioural also) means which ensures constant body temperature, constant osmotic concentration, etc. All birds and mammals and a very few lower vertebrate and invertebrate species are indeed capable of such regulation (thermoregulation and osmoregulation).
Question 39: Assertion (A): The Monarch butterfly feeds on poisonous weeds during its caterpillar stage.
Reason (R): It helps butterfly to become distasteful to the predator.
- a. (A) is true (R) is false
- b. (A) is true and (R) is it correct explanation
- c. Both (A) and (R) are false
- d. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The butterfly acquires this chemical during its caterpillar stage by feeding on a poisonous weed. The monarch butterfly is highly distasteful to its predator (bird) because of a special chemical present in its body.
Question 40: From the given options, identify the correct combination of population interactions that correspond to the symbols given here.
- a. Parasitism Competition Mutualism
- b. Predation Competition Commensalism
- c. Mutualism Competition Commensalism
- d. Mutualism Parasitism Amensalism
- Answer: (c)
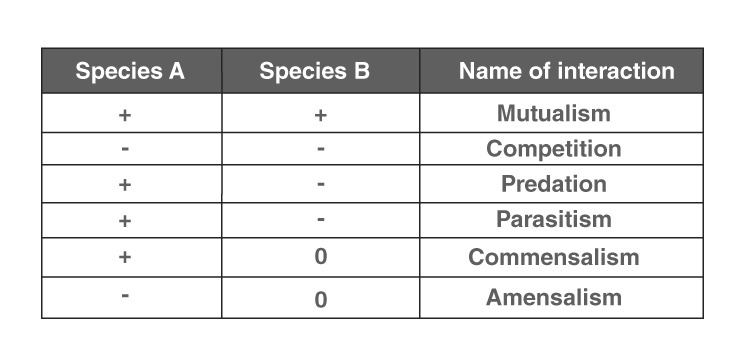 Both the species benefit in mutualism and both lose in competition in their interactions with each other. In both parasitism and Predation, only one species benefits (parasite and predator, respectively) and the interaction is detrimental to the other species (host and prey, respectively). The interaction where one species is benefitted and the other is neither benefitted nor harmed is called commensalism.
Both the species benefit in mutualism and both lose in competition in their interactions with each other. In both parasitism and Predation, only one species benefits (parasite and predator, respectively) and the interaction is detrimental to the other species (host and prey, respectively). The interaction where one species is benefitted and the other is neither benefitted nor harmed is called commensalism.
Question 41: The nourishing cells in the Seminiferous tubules are
- a. Follicular cells
- b. Leydig cells
- c. Sertoli cells
- d. Spermatogonial cells
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The large sustentacular cells that extend from the capsule to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule are called Sertoli cells. They serve to support, nourish, and regulate the maturation of sperm cells during spermatogenesis.
Question 42: If in a normal Menstruating woman, menses occur 5th April, what will be expected date of Ovulation?
- a. 10th April
- b. 18th April
- c. 29th April
- d. 14th April
Solution:
Answer: (b)
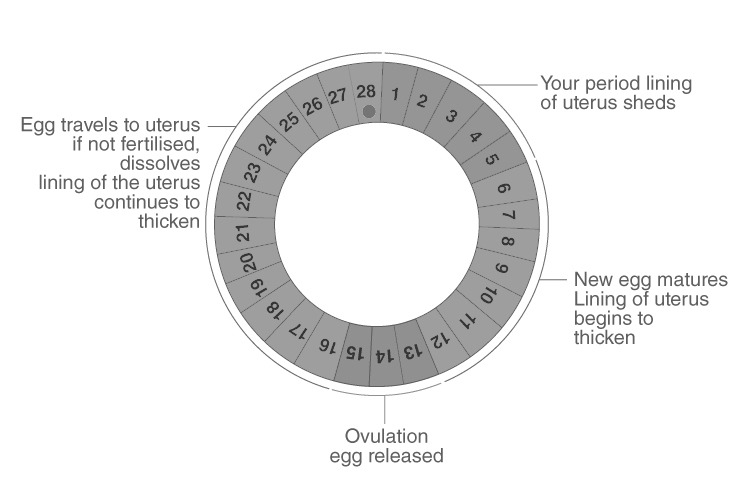
Normal menstruating woman, menses occur on 5th April. The expected date of ovulation is 18th April.
Question 43: Identify the cells represented as P, Q, R and S in the given schematic representation of spermatogenesis.
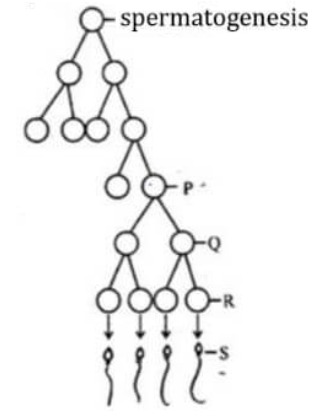
- a. P – Spermatozo
Q – Spermatid
R – Secondary Spermatocyt
S – Primary Spermatocyt
- b. P – Primary Spermatocyt
Q – Secondary Spermatocyt
R – Spermatid
S – Spermatozo
- c. P – Secondary Spermatocyt
Q – Spermatid
R – Spermatozo
S – Primary Spermatocyt
- d. P – Secondary Spermatocyt
Q – Primary Spermatocyt
R – Spermatozo
S – Spermatid
- Answer: (b)
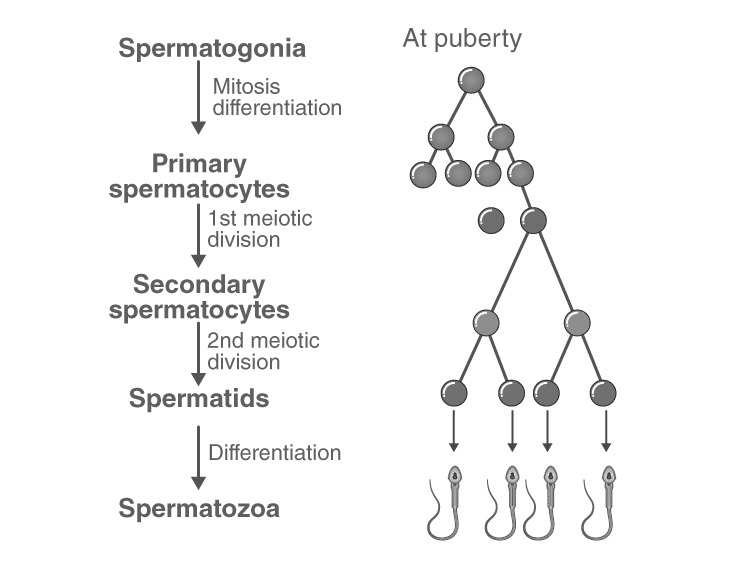 Spermatogenesis is the process of the production of sperms from the immature germ cells in males. The correct sequence is P-Primary Spermatocyte, Q-Secondary Spermatocyte.R- Spermatid and S-Spermatozoa.
Spermatogenesis is the process of the production of sperms from the immature germ cells in males. The correct sequence is P-Primary Spermatocyte, Q-Secondary Spermatocyte.R- Spermatid and S-Spermatozoa.
Question 44: The method of natural contraception which requires correct knowledge of Menstrual cycle is
- a. Periodic Abstinence
- b. Lactational Amenorrhoea
- c. IUDs – Intrauterine Devices
- d. Coitus interrupts
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Natural methods work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting. Periodic abstinence is one such method in which the couples avoid or abstain from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle when ovulation could be expected. As chances of fertilization are very high during this period, it is called the fertile period. Therefore, by abstaining from coitus during this period, conception could be prevented.
Question 45: A childless couple visit Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ARTs) centre to get assistance to have a child. On diagnosis, it was noticed that there was a low sperm count in the male partner. Which of the following strategy of ART is most suitable in this case?
- a. Gamete Intra-Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
- b. Artificial Insemination (Al)
- c. Zygote Intra-Fallopian Transfer
- d. In-vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Infertility cases either due to the inability of the male partner to inseminate the female or due to very low sperm counts in the ejaculates could be corrected by artificial insemination (AI) technique. In this technique, the semen collected either from the husband or a healthy donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus of the female.
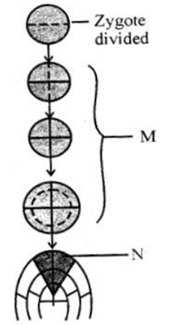
- a. M is a geometric phase and N is an arithmetic phase
- b. Both M and N are arithmetic phases
- c. M is an arithmetic phase and N is a geometric phase
- d. Both M and N are geometric phases
Solution:
Answer: (a)
In the figure, the zygote undergoes mitotic division. In the initial stage or the M stage, every progeny cell retains its capacity to divide and form progeny cells. Here no cells are undergoing differentiation. So, here the division occurs in a 2n manner, growth in unicellular organisms and certain higher plants. The graph plotted here is exponential gradually moving to sigmoid.
In stage N, not all the progeny cells retain their capacity to divide; some stop division and undergo differentiation. So, here the division occurs as 2,4,6,8 i.e. in an arithmetic progression. Example: growth in root and stem. The graph plotted here is linear.
Question 47: Indigestion of fats in humans may be an indication of
- a. Intestinal ulcers
- b. Under secretion of saliva
- c. Inflammation of the liver
- d. Under secretion of amylopsin
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Indigestion is often a sign of an underlying problem, such as ulcers, or gallbladder disease i.e. indigestion of fats in human may be an indication of inflammation of the liver.
Question 48: Choose the correct statement from the following :
- a. Erythroblastosis foetalis may result when the foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
- b. Histamine, Serotonin and Heparin are secreted by basophils
- c. Atherosclerosis is often referred to as angina pectoris
- d. Person with blood group AB can donate blood to a person with blood group A
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Erythroblastosis fetalis classically results from incompatibility, which may develop when a woman with Rh-negative blood is impregnated by a man with Rh-positive blood and conceives a foetus with Rh-positive blood, sometimes resulting in haemolysis.
Mast cells are a type of granular basophil cells in the connective tissue that releases heparin, histamine and serotonin during inflammation and allergic reactions.
Coronary Artery Disease, often referred to as atherosclerosis, affects the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. It is caused by deposits of calcium, fat, cholesterol and fibrous tissues, which makes the lumen of arteries narrower. Angina is also called ‘angina pectoris’. A symptom of acute chest pain appears when no enough oxygen is reaching the heart muscle. Angina can occur in men and women of any age but it is more common among the middle-aged and elderly. It occurs due to the conditions that affect blood flow.
Donors with blood type AB can donate to recipients with blood type AB only.
Question 49: In a blind spot of the human eye
- a. Both cones and rods are absent
- b. Only cones are absent
- c. Both cones and rods are present
- d. Only rods are absent
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) are not present in that region and hence, it is called the blind spot.
Question 50: A boy after attaining sexual maturity shows muscular growth, growth of facial and axillary hair, aggressiveness and low pitch of voice. These changes are attributed to ___ hormone.
- a. Estrogen
- b. Testosterone
- c. Secretin
- d. Glucagon
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Testosterone is linked to many of the changes seen in boys during puberty (including an increase in height, body and pubic hair growth, and changes in sexual and aggressiveness and low pitch of voice).
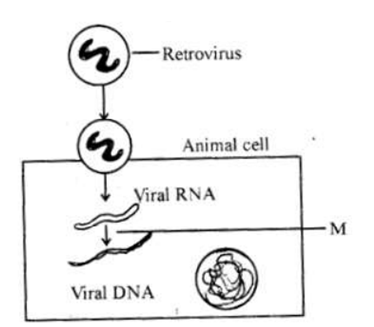
Question 51: Identify the enzyme that catalyses the step labelled as ‘M’ in the given schematic representation of Replication of Retrovirus
- a. Reverse transcriptase
- b. RNA Polymerase
- c. Recombinase
- d. DNA ligase
Solution:
Answer: (a)
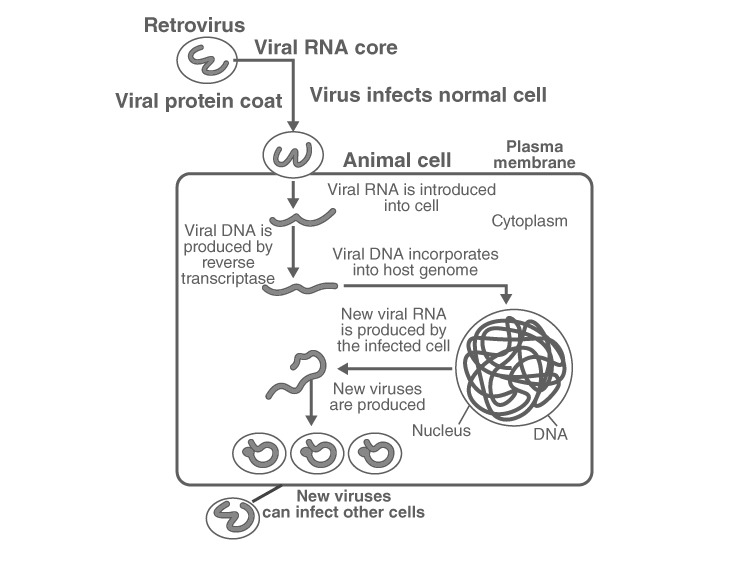
Retroviruses infect the host cell and inject their genetic material, RNA, into the host cell. Inside the host cell, viral DNA is produced from the viral RNA is produced by the enzyme reverse transcriptase which used RNA as a template to synthesis DNA. The viral DNA gets incorporated into the host genome and is replicated as the host genome replicates. Viral RNA is produced from the replicated viral DNA by transcription which then forms new virus particles. The viruses are then released which infect other cells.
Question 52: In animal breeding, the maximum genetic variations can be achieved through.
- a. Inbreeding
- b. Outcrossing
- c. Interspecific hybridization
- d. Crossbreeding
Solution:
Answer: (c)
When breeding is between animals of the same breed it is called inbreeding.
Out-crossing: This is the practice of mating of animals within the same breed, but having no common ancestors on either side of their pedigree up to 4-6 generations.
Interspecific hybridization: In this method, male and female animals of two different species are mated. The maximum genetic variations are present in it. In some cases, the progeny may combine desirable features of both the parents, and maybe of considerable economic value, e.g., the mule.
Cross-breeding: In this method, superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed.
Question 53: The oil content and quality of groundnut variety was improved by plant breeding technique. This is an example of;
- a. Bioremediation
- b. Biomagnification
- c. Biodegradation
- d. Biofortification
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Biofortification refers, breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals, or higher protein and healthier fats – is the most practical means to improve public health.
Breeding for improved nutritional quality is undertaken with the objectives of improving &ndash.
Protein content and quality.
Oil content and quality.
Vitamin content; and
Micronutrient and mineral content.
Question 54: Microbes like spirulina can be a good alternative to the conventional sources of proteins for human nutrition because
- a. Their proteins are different from plant proteins
- b. they give more biomass in less time
- c. they have a high fibre content
- d. they are produced using synthetic fertilizers
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Microbes like spirulina can be grown easily on materials like wastewater from potato processing plants (containing starch), straw, molasses, animal manure and even sewage, to produce large quantities and can serve as food rich in protein, minerals, nutrition because of a high rate of biomass production and growth in less time.
Question 55: Consider the following morphological biochemical or physiological characteristics of plants.
- i. Presence of hairy leaves
- ii. Production of more nectar is flower
- iii. High sugar content in plant parts
- iv. Presence of higher aspartic acid concentration.
- Choose the correct combination of statements which give natural resistance to plants against insect pests:
- a. iii and iv
- b. i and ii
- c. i and iv
- d. ii and iii
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Insect resistance in host crop is due to morphological, biochemical or physiological characteristics. Some characters which make the plants resistance to insects are;
High aspartic acids.
Presence of hairy leaves.
Low nitrogen and sugar content in maize make them resistant to stem borers.
Production of less nectar in flower.
Question 56: Identify the odd one among the following disorders:
- a. Haemophilia
- b. Sickle-cell -Anaemia
- c. Phenyl Ketonuria
- d. Thalassemia
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Most common and prevalent Mendelian disorders are Haemophilia, Cystic fibrosis, Sickle-cell anaemia, Colour blindness, Phenylketonuria, Thalassemia, etc. It is important to mention here that such Mendelian disorders may be dominant or recessive. Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease, which shows it’s a transmission from unaffected carrier female to some of the male progeny. Another disease is an autosomal recessive disorder.
Question 57: From the chromosomal complements given below, identify the one which shows female heterogamety.
- a. XX – XO
- b. XX – XY
- c. XX – XXY
- d. ZZ – ZW
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Birds show the different mechanism of sex determination. In this case, the total number of chromosome is the same in both males and females. But two different types of gametes in terms of the sex chromosomes are produced by females, i.e., female heterogamety. In order to have a distinction with the mechanism of sex determination described earlier, the two different sex chromosomes of a female bird have been designated to be the Z and W chromosomes. In these organisms, the females have one Z and one W chromosome, whereas males have a pair of Z-chromosomes besides the autosomes.
Question 58: In Morgan’s experiment with Drosophila, when a yellow bodied white-eyed female was crossed with brown bodied red-eyed male and their F1 Progeny were intercrossed. What was the percentage of recombinants in the F2 generation?
- a. 62.8%
- b. 98.7%
- c. 1.3%
- d. 37.2%
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Morgan hybridized yellow-bodied, white-eyed females to brown-bodied, red-eyed males and intercrossed their F1 progeny. He observed that the two genes did not segregate independently of each other and the F2 ratio deviated significantly from the 9:3:3:1. Morgan and his group also found that even when genes were grouped on the same chromosome, some genes were very tightly linked (showed very low recombination) while others were loosely linked (showed higher recombination). For example, he found that the genes white and yellow were very tightly linked and showed only 1.3 per cent recombination while white and miniature wing showed 37.2 per cent recombination.
Question 59: In the following symbols, used in human pedigree analysis, identify the symbol that denotes consanguineous mating.
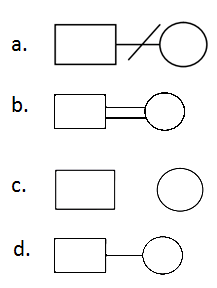
Solution:
Answer: (b)

Question 60: Which of the following Nitrogen bases is found only in DNA?
- a. Cytosine
- b. Adenine
- c. Thymine
- d. Guanine
Solution:
Answer: (c)
DNA is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides. The deoxyribonucleotides are made up of phosphoric acid and deoxyribonucleosides. The deoxyribonucleosides are made up of deoxyribose sugars and nitrogenous bases. The nitrogenous bases present in DNA are purine (adenine or guanine) and pyrimidine (cytosine or thymine).
Thymine is specifically found in DNA.
Uracil is found in RNA.
Guanine and cytosine are found in DNA as well as in RNA.
- KCET 2019 Physics Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Maths Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Physics Paper
- KCET 2020 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Mathematics Questions Paper
- KCET Biology Examination 2021 Paper
- KCET – 2021 TEST PAPER
- IISER MOCK TEST – 4
- IISER MOCK TEST – 3
- IISER MOCK TEST – 2
- IISER MOCK TEST – 1
- KCET Mathematics- 2021 Test Paper
- KCET Chemistry – 2021 TEST PAPER
- KCET Physical – 2021 TEST PAPER
- KCET Biology Examination 2021 Paper
- KCET 2020 Mathematics Questions Paper
- KCET 2020 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2020 Physics Paper
- KCET 2020 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Biology Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Chemistry Paper with Solutions
- KCET 2019 Maths Paper with Solutions
